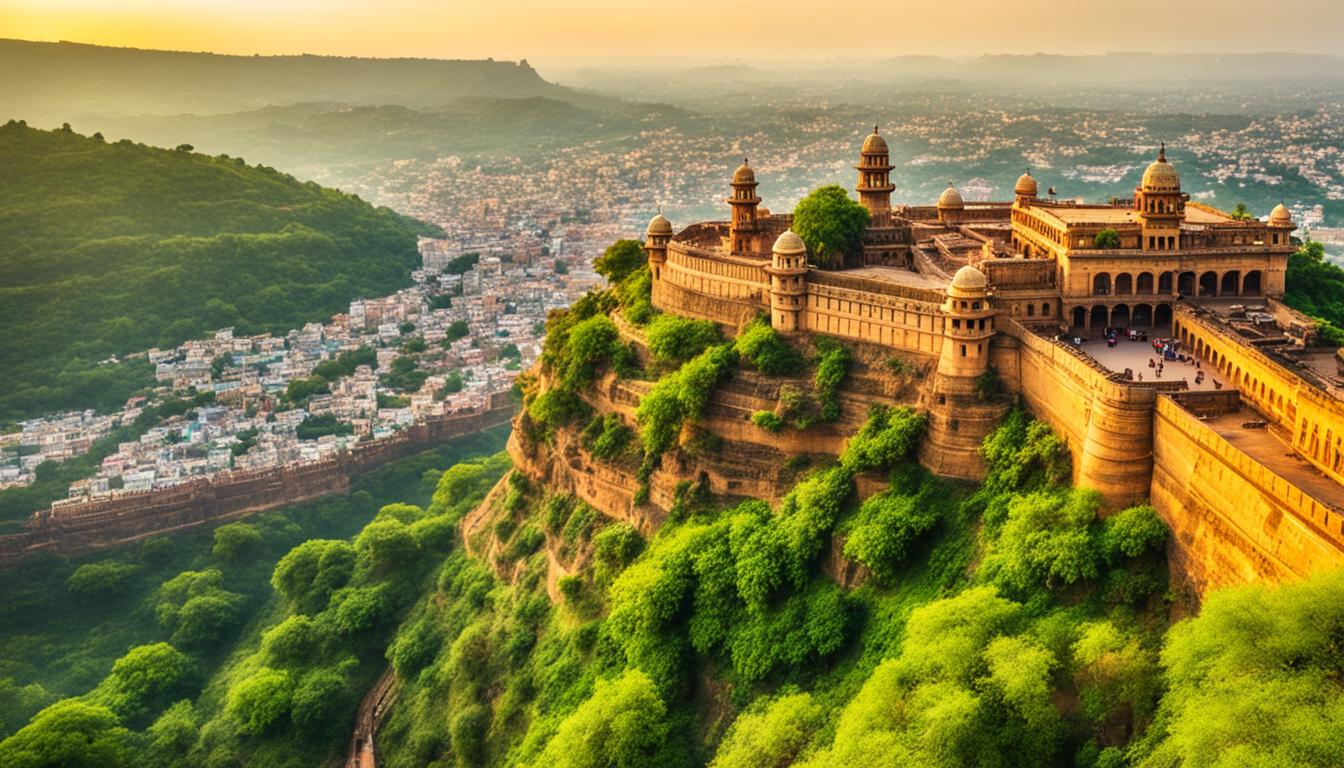

Explore Gwalior Fort’s Majestic History & Views
Imagine standing at the edge of a towering fortress, looking out over a breathtaking cityscape that stretches as far as the eye can see. The sun glistens off the sandstone walls, casting a warm glow over the ancient architecture. This is Gwalior Fort, a remarkable testament to India’s rich history and architectural brilliance.
Located in the city of Gwalior, India, the fort has stood tall for centuries, withstanding invasions, wars, and the test of time. Its origins date back to the 6th century, and it has been ruled by various dynasties including the Huns, Prathiharas, Mughals, and Marathas.
Perched on a rocky outcrop of Vindhyan sandstone, the fort offers commanding views of the surrounding countryside. Its grand and imposing architecture, with moss-covered domes, faded doors, and intricately carved walls, tells stories of conquerors and kings.
As you explore the fort, you’ll come across temples, palaces, and museums that offer a glimpse into the past. The Man Singh Palace, with its mosaic tiles and intricate carvings, stands as a testament to the opulence of the Rajput rulers. The Teli Ka Mandir, a unique blend of South Indian and North Indian architectural styles, showcases the intricacies of ancient craftsmanship.
But Gwalior Fort isn’t just a collection of buildings. It’s a living testament to history. The fort has witnessed significant events, from the capture of Guru Hargobind by Mughal Emperor Jahangir to conflicts between the British and Scindias. It’s a place where the past comes alive, immersing you in a world of stories and legends.
So, pack your bags and prepare to step into the majestic world of Gwalior Fort. With its stunning views, rich history, and architectural wonders, it promises an experience like no other.
History of Gwalior Fort
Gwalior Fort has a rich and ancient history that dates back to the 6th century. The exact origins of the fort are uncertain, but it is believed to have been commissioned by Raja Suraj Sen Pal. Over the centuries, the fort changed hands multiple times, with rulers like the Mauryas, Shungas, Kushanas, Guptas, Huns, and Gurjara Pratiharas.
The Tomar dynasty played a significant role in the construction and expansion of the fort in the 14th century. The Mughals used the fort as a prison, and it was also involved in the events of the Great Mutiny of 1857. The British took control of the fort after the defeat of the Marathas in 1818, and it later became a part of independent India.
Key Events and Rulers
- 6th century: Gwalior Fort is believed to be commissioned by Raja Suraj Sen Pal.
- Mauryas, Shungas, Kushanas, Guptas, Huns, and Gurjara Pratiharas rule over the fort.
- 14th century: Tomar dynasty plays a significant role in the fort’s construction and expansion.
- Mughals use the fort as a prison during their reign.
- 19th century: The fort witnesses events of the Great Mutiny of 1857.
- 1818: British take control of the fort after defeating the Marathas.
- 20th century: Gwalior Fort becomes a part of independent India.
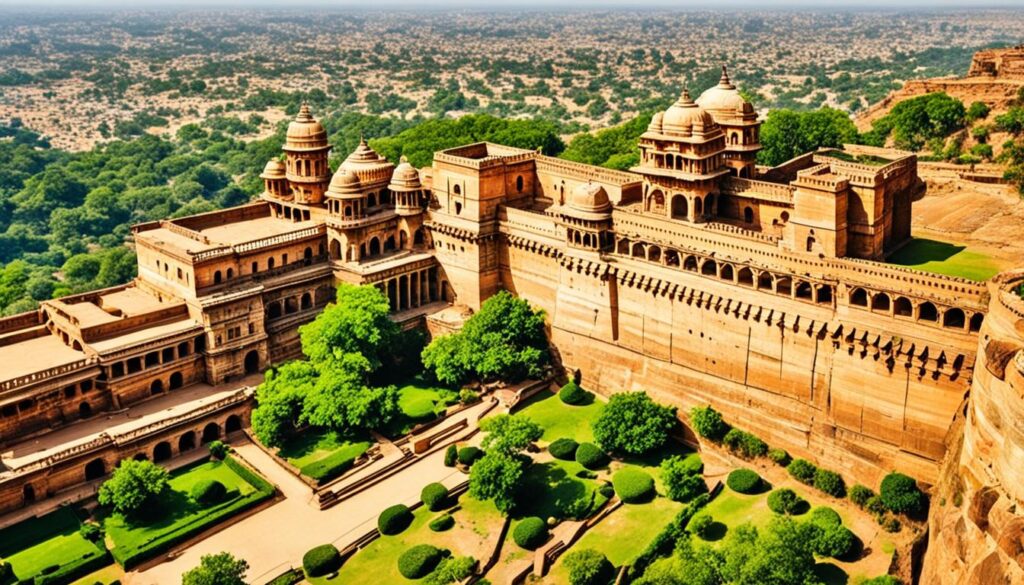
Architecture of Gwalior Fort
The architecture of Gwalior Fort is a testament to the grandeur and artistic richness of its history. The fort showcases a harmonious blend of various architectural styles that have evolved over different periods and under the rule of various dynasties.
Made primarily of sandstone, Gwalior Fort features magnificent structures that stand as a testament to the architectural prowess of ancient India. Some of the notable architectural marvels within the fort include:
- Man Singh Palace: The Man Singh Palace is renowned for its intricate carvings, lattice-screens, and vibrant blue and yellow tile decorations. It stands as a remarkable example of Mughal and Rajput architecture.
- Teli Ka Mandir: Teli Ka Mandir is a unique temple within the fort that showcases a striking combination of South Indian and North Indian architectural elements. Its towering shikhara (spire) and ornate sculptures make it a must-see for visitors.
- Saas-Bahu Temple: The Saas-Bahu Temple is dedicated to both Lord Vishnu and Lord Shiva. It is known for its exquisite carvings that adorn the temple’s walls and pillars, showcasing the finesse of medieval Indian architecture.
In addition to these impressive structures, Gwalior Fort houses underground chambers, amphitheatres, and courtyards, adding to its architectural grandeur. The exterior of the fort is adorned with intricate sculptures, floral motifs, and depictions of various animals, which further enhance its aesthetic appeal.
Must-see Monuments Inside Gwalior Fort
Gwalior Fort is home to several magnificent monuments that are a testament to its rich history and architectural grandeur. These attractions are a must-visit during your trip to the fort, offering a glimpse into the diverse cultural influences and remarkable craftsmanship of the rulers.
Sculptures of Jain Tirthankaras in Gopachal Hill
The sculptures of Jain Tirthankaras, located in Gopachal Hill within Gwalior Fort, are a breathtaking sight to behold. Among them, the largest idol stands tall at an impressive height of 42 feet. These intricately carved sculptures showcase the exquisite artistry and religious significance of Jainism.
Man Singh Palace
Man Singh Palace, a grand structure within Gwalior Fort, is a striking example of architectural brilliance. Adorned with mosaic tiles, lattice-screens, and underground passages, this palace offers a fascinating glimpse into the opulent lifestyle of the past rulers. It exudes an aura of regality and is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the region.
Teli Ka Mandir
Teli Ka Mandir, another notable attraction within Gwalior Fort, stands out with its unique architectural style. This temple beautifully combines elements of South Indian and North Indian architectural traditions, creating a harmonious blend of aesthetics. Its towering pinnacle and intricate carvings make it a must-see marvel within the fort.
Saas-Bahu Temple
The Saas-Bahu Temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu and Lord Shiva, is a gem of religious architecture within Gwalior Fort. Known for its exquisite carvings and intricate detailing, this temple epitomizes the skill and craftsmanship of the bygone era. Its serene ambience and spiritual significance make it a favorite among visitors.
Other significant attractions within Gwalior Fort include Kirti Mandir, Vikramaditya Palace, and Gujari Mahal. Each monument has its own historical and architectural significance, adding to the rich tapestry of Gwalior Fort. Exploring these attractions is a rewarding experience that allows you to delve into the captivating stories of the past and appreciate the legacy left behind by the visionary rulers.

| Monument | Description |
|---|---|
| Scultpures of Jain Tirthankaras in Gopachal Hill | A collection of stunning sculptures, with the largest idol reaching a height of 42 feet. |
| Man Singh Palace | A grand palace showcasing mosaic tiles, lattice-screens, and underground passages. |
| Teli Ka Mandir | A unique temple blending South Indian and North Indian architectural styles. |
| Saas-Bahu Temple | An intricately carved temple dedicated to Lord Vishnu and Lord Shiva. |
| Kirti Mandir | A temple dedicated to Jains, housing several beautiful idols. |
| Vikramaditya Palace | A palace with historical significance and architectural splendor. |
| Gujari Mahal | A magnificent palace showcasing the rich cultural heritage of Gwalior. |
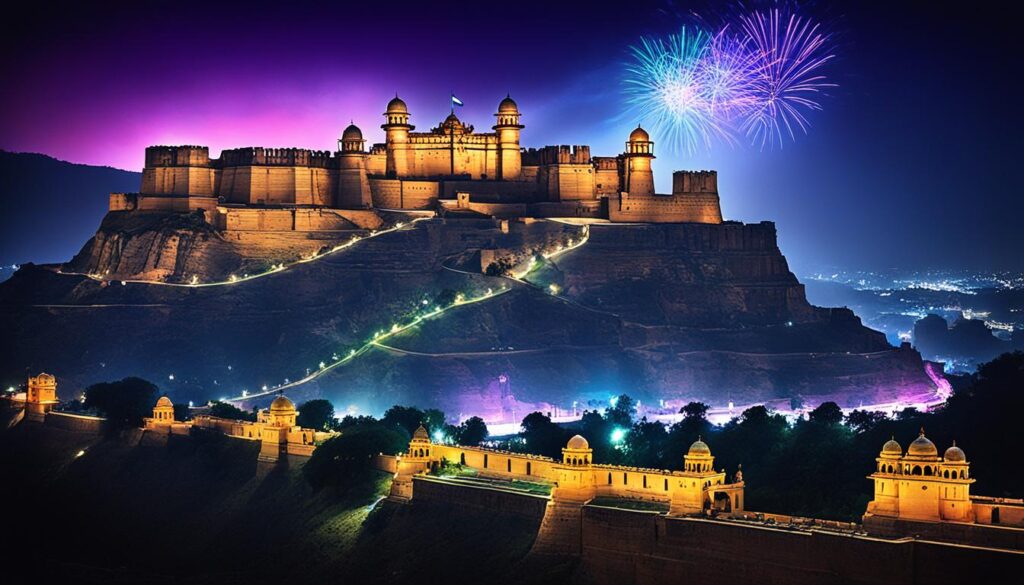
Light And Sound Show At Gwalior Fort
The light and sound show at Gwalior Fort is a mesmerizing experience that brings the history and legends of the fort to life. Taking place in the Man Mandir amphitheater, this captivating show is a must-see for visitors looking to delve deeper into the story of Gwalior Fort.
The show, available in both Hindi and English, starts at 7:30 PM in Hindi and 8:30 PM in English. Lasting for approximately 45 minutes, it offers a vivid narration of the fort’s rich history, immersing the audience in tales of ancient battles, royal dynasties, and cultural heritage. The combination of visual effects, dramatic storytelling, and synchronized lighting creates a truly enchanting atmosphere.
If you’re planning a visit to Gwalior Fort, it’s highly recommended to check the schedule and timings of the light and sound show in advance. Don’t miss this opportunity to explore the fort’s fascinating past in a unique and engaging way.

| Show Timings | Language |
|---|---|
| 7:30 PM | Hindi |
| 8:30 PM | English |
Facts About Gwalior Fort
Gwalior Fort, located in the city of Gwalior, is one of the largest forts in India. With its massive structure and historical significance, it stands as a symbol of India’s rich heritage. One fascinating fact about Gwalior Fort is that it is home to the second oldest reference to the number “Zero” in mathematics. This ancient inscription dates back centuries and showcases the advanced knowledge and achievements of ancient Indian mathematicians.
Another noteworthy aspect of the fort is the presence of inscriptions that are approximately 1500 years old. These inscriptions provide valuable historical information about the fort’s past and the dynasties that have ruled over it. It’s truly remarkable to witness these ancient writings that have withstood the test of time and continue to captivate visitors.
Believed to have existed since the 6th century, Gwalior Fort is one of the oldest forts in India. It has withstood various invasions and witnessed significant historical events throughout its long history. The fort not only showcases awe-inspiring architecture but also houses numerous palaces, temples, and water tanks, offering a glimpse into the grandeur of its past. Exploring Gwalior Fort is an immersive experience that allows visitors to delve into the rich history and architectural brilliance of ancient India.
Source Links
- https://traveltriangle.com/blog/gwalior-fort/
- https://thefloatingpebbles.com/gwalior-fort/
- https://www.fabhotels.com/blog/gwalior-fort-madhya-pradesh/
Leave a Reply